Major Challenges in Travel API Integration

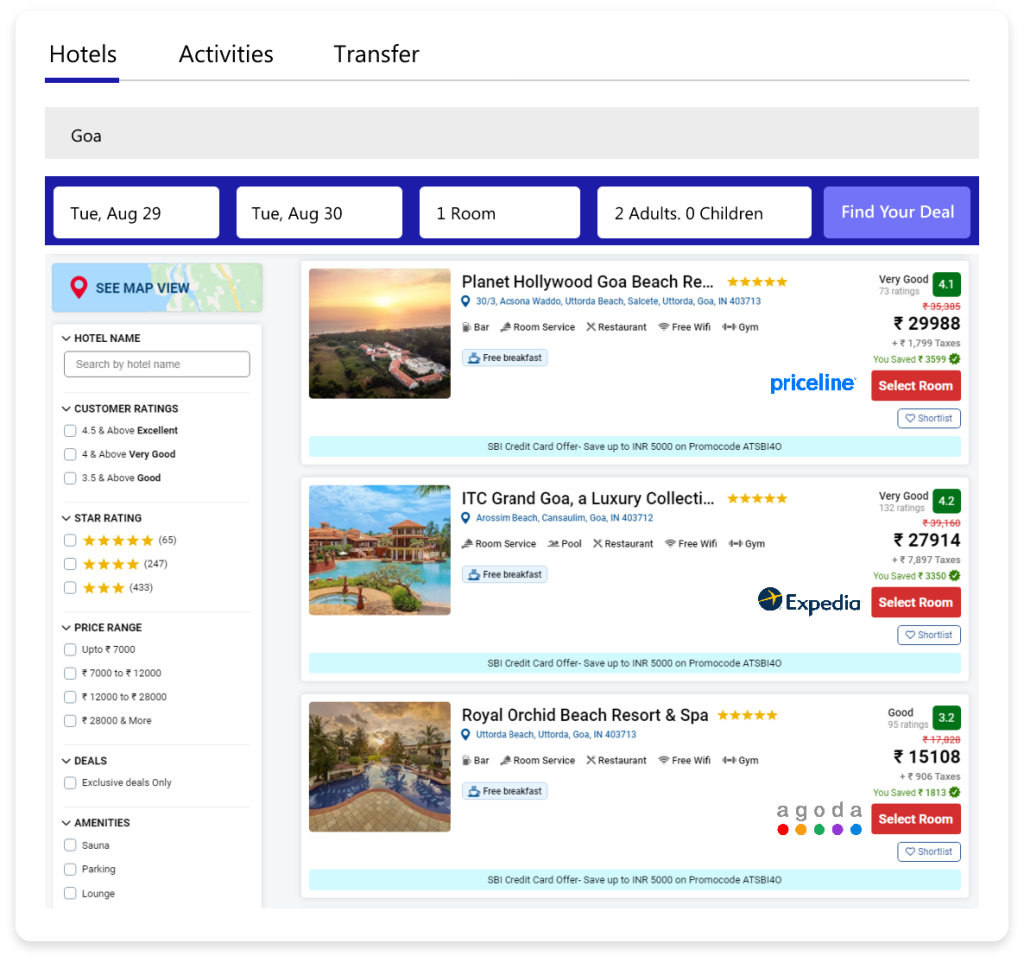
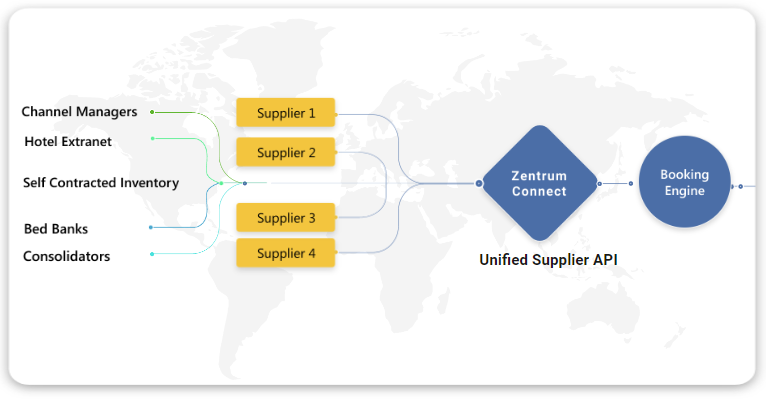
Challenges Faced by OTA during API Integration APIs allow travel agencies to connect with various suppliers, such as airlines, hotels, and car rental services, to provide real-time availability, pricing, and booking functionality. While the benefits are undeniable, implementing API integrations comes with its own set of challenges. For example, a travel agency software integrated with travel APIs can access real-time travel schedules, seat availability, and fare details from various airlines. Similarly, hotel APIs provide room availability, rates, and booking options. APIs play a vital role in automating workflows, reducing manual processes, and offering customers seamless booking experiences. With APIs, travel agencies can aggregate services from multiple vendors into one interface, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction. Benefits of Travel Agency Software API Integration Before diving into the challenges, it’s important to understand the key advantages of travel API integration: Real-Time Access: APIs provide real-time data for travels, hotels, and other travel services, ensuring up-to-date inventory and pricing. Expanded Inventory: By integrating multiple APIs, agencies can offer a wider range of services from various suppliers. Customization: Travel agency software can use APIs to create tailor-made travel packages by combining travels, accommodations, and tours. Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces the need for manual interventions, saving time and operational costs. Improved User Experience: APIs enable smooth booking experiences for customers, with features like dynamic pricing and instant confirmations. Challenges in Travel Agency Software API Integration Despite the benefits, travel API integration poses several challenges that can hinder its successful implementation: Data Consistency and Accuracy APIs rely on suppliers to provide accurate and consistent data. Discrepancies in pricing, availability, or booking details can lead to errors, resulting in customer dissatisfaction. Example: A travel API might show seats as available during the booking process but display an error at the payment stage due to outdated inventory. Latency Issues High latency during API calls can slow down response times, causing delays in displaying results to customers. This is especially problematic during peak travel seasons or when multiple users are accessing the system simultaneously. Example: If hotel search results take too long to load, customers may abandon the booking process. Complexity in Integration Integrating multiple APIs from different suppliers can be technically complex. Each API has its own structure, protocols, and data formats, requiring significant customization and development efforts. Example: Travel APIs and car rental APIs often use different naming conventions and data schemas, making it challenging to unify them into one system. Dependency on Third-Party Providers Travel agencies are highly dependent on API providers for maintaining data accuracy, uptime, and overall performance. Downtime or errors on the provider’s end can directly impact the agency’s operations. Example: If an airline’s API goes offline, the agency may not be able to process bookings, leading to lost revenue. Costs and Licensing API providers often charge licensing fees or commission-based charges, which can add up, especially when integrating multiple APIs. Agencies must carefully manage these costs to maintain profitability. Example: Popular APIs like Amadeus or Sabre often come with significant licensing fees, impacting small travel agencies’ budgets. Security Concerns APIs handle sensitive customer information, such as payment details and personal data. Any vulnerabilities in API integration can expose this data to security threats like hacking or unauthorized access. Example: An insecure API connection could lead to a data breach, compromising customer trust and agency reputation. Scalability and Maintenance As the business grows, agencies need their software to scale and handle increased traffic and API requests. Maintaining API integrations, especially when providers update their systems, can be resource-intensive. Example: A travel agency expanding its operations may face challenges in scaling its API infrastructure to handle higher volumes of transactions. Solutions to Overcome Travel Agency Software API Integration Challenges For successful API integration, travel agencies need strategic planning and the right tools. Here are practical solutions to address the challenges mentioned above: Implement a Middleware Layer A middleware layer acts as a bridge between the travel agency software and multiple APIs. It standardizes data formats, protocols, and workflows, making integration easier and more efficient. Benefits: Reduces complexity in managing multiple APIs. Provides a centralized platform for monitoring and troubleshooting API issues. Example: A middleware solution can unify travel, hotel, and car rental APIs into a single interface for the travel agency software. Optimize API Performance Use caching mechanisms and load balancing to reduce latency and improve response times. Caching stores frequently accessed data, such as popular travel routes or hotel availability, reducing the need for repeated API calls. Benefits: Faster response times for users. Reduces the load on API servers during peak traffic. Example: Implementing a caching solution for frequently searched destinations during the holiday season can enhance user experience. Choose Reliable API Providers Partner with reputable API providers known for their reliability, uptime, and support services. Perform due diligence by checking reviews, uptime statistics, and available support channels. Benefits: Ensures consistent data accuracy and performance. Reduces dependency risks associated with unreliable providers. Example: Providers like Sabre, Amadeus, and Expedia Partner Solutions offer robust and well-documented APIs. Monitor and Test Regularly Implement monitoring tools to track API performance, uptime, and error rates. Regular testing helps identify potential issues and ensures seamless integration. Benefits: Detects and resolves issues proactively. Improves overall system stability. Example: Use tools like Postman or API monitoring services to test endpoints and measure response times. Prioritize Security Measures Secure API connections with encryption protocols like HTTPS and use authentication mechanisms such as OAuth 2.0 to protect sensitive data. Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities. Benefits: Protects customer data and builds trust. Reduces the risk of cyber threats. Example: Ensure that payment gateways integrated via APIs comply with PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). Manage Costs Effectively Negotiate pricing with API providers and evaluate usage-based models to optimize costs. Consider using free or lower-cost APIs for less critical services. Benefits: Keeps operational costs under control. Allows for more sustainable scaling of services. Example: Use a combination of premium APIs for core services and open-source
Integrating Payment Systems into Your Travel Agency Software

Integrating Payment Systems into Your Travel Agency Software The travel industry thrives on customer convenience and satisfaction. An integral part of that is ensuring that customers have a frictionless way to pay for services. Integrating a robust payment system into your travel agency’s software can transform your operations, making transactions faster, more secure, and capable of accommodating diverse payment methods. In the fast-paced world of travel, seamless and secure payment processes are critical for an exceptional customer experience. Integrating a payment system into your travel agency software ensures smooth transactions, enhances trust, and fosters customer loyalty. This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits, challenges, and best practices for effectively integrating payment systems. Benefits of Payment System Integration a. Improved Customer Experience A streamlined payment process is fundamental to customer satisfaction. The ability to quickly complete a transaction means fewer cart abandonments and higher conversion rates. For instance, a study by the Baymard Institute found that nearly 18% of shoppers abandon their carts due to a long or complicated checkout process. A seamless integration reduces these friction points. b. Enhanced Security and Compliance Integrating a trusted payment system comes with built-in security protocols such as tokenization and encryption, which protect sensitive data. Compliance with global standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) ensures that your agency operates within legal requirements, safeguarding both you and your customers. c. Expanded Payment Options Offering various payment methods, such as credit cards, e-wallets, bank transfers, and even cryptocurrencies, appeals to a global audience. This is especially important for travel agencies, as clients often come from different parts of the world with varying payment preferences. Statistic: According to Worldpay’s Global Payments Report, over 40% of global online transactions are made via digital wallets. Types of Payment Systems a. Payment Gateways vs. Payment Processors Understanding the difference between payment gateways and processors is crucial: Payment Gateways: Serve as the intermediary between your travel agency’s software and the financial institution. They encrypt payment information, verify its authenticity, and send it to the bank for approval. Examples include Authorize.Net and Stripe. Payment Processors: Handle the transaction’s backend by transferring data between the bank and your merchant account. Often, a complete system will use both a gateway and a processor. b. Examples of Popular Systems Stripe: Offers extensive APIs for customization, making it ideal for agencies wanting tailored solutions. PayPal: Provides ease of use and consumer trust, suitable for agencies looking to add credibility. Square: Known for its user-friendly interface and solid support for small to mid-sized businesses. Insight: If your target market spans multiple regions, select a provider that supports a variety of currencies and local payment methods to prevent conversion issues and high transaction fees. Also Read: Top Benefits of Travel Agency Software for Automated Bookings Key Considerations Before Integration a. Compatibility with Existing Software Evaluate the technical specifications of your current travel agency software. Most popular travel platforms support third-party integrations via APIs or plug-ins, but it’s essential to ensure your choice is compatible to avoid costly development time. b. Security Protocols and Compliance Choose a system that not only supports SSL certificates but also uses advanced authentication methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and tokenization. Compliance is non-negotiable for protecting user data. c. User Experience and Checkout Flow The payment process should be intuitive. A cluttered or overly complex interface can lead to abandoned bookings. Ensure minimal steps between selecting a service and completing the payment. Best Practice: Conduct user testing to identify any bottlenecks in the checkout process. Tools like Hotjar can provide heatmaps and session recordings for optimization. Step-by-Step Guide to Integrating a Payment System Step 1: Choose the Right Payment Provider Your first step should be researching the providers that best align with your business needs. Consider factors such as transaction fees, customer support, global reach, and customization capabilities. Checklist: Support for multi-currency Transparent fee structures Responsive customer support Step 2: Set Up API Integration Once you’ve selected a provider, your development team will need to integrate the payment system’s API. This may involve coding and setting up webhooks for transaction statuses. Pro Tip: Use sandbox environments provided by many payment providers to test the integration without real money transfers. Step 3: Implement Security Measures Security is paramount. Implement SSL/TLS certificates for data encryption and consider integrating 3D Secure for an extra layer of cardholder authentication. Tip: Enable address verification services (AVS) to verify billing addresses for added fraud protection. Step 4: Test and Optimize Run comprehensive tests for all types of transactions, including successful payments, declined cards, refunds, and partial payments. Testing helps identify any potential issues before going live. Checklist for Testing: Verify multi-device compatibility (desktop, mobile, tablet) Test various payment methods (credit cards, digital wallets, etc.) Simulate high transaction loads to test the system’s response under pressure. Also Read Travel Agency Software API Integration: Challenges and Solutions Challenges and How to Overcome Them a. Technical Issues Integrating a payment system may lead to unexpected bugs or compatibility issues. Collaborating with experienced developers who understand both your travel software and the payment system can alleviate these technical difficulties. Solution: Work with payment providers that offer strong developer support, including detailed documentation and responsive technical teams. b. Regulatory Challenges Navigating regulations like PCI DSS and PSD2 (for European transactions) can be daunting. Partnering with a payment provider familiar with these regulations can help you stay compliant. Advice: Periodically audit your payment systems and consult legal experts to ensure ongoing compliance. Best Practices for a Successful Integration a. Regular Updates and Maintenance The digital payment landscape changes rapidly. Regularly update your software and payment system to patch vulnerabilities and add new features. Tip: Schedule periodic reviews of your payment process to assess whether it aligns with the latest security standards and customer expectations. b. Transparent Policies Display clear payment policies, including refunds and cancellations. Transparency reduces disputes and chargebacks, contributing to smoother operations. Example: Use straightforward language and bullet points for policies on your payment